The battery is an essential requirement for most electrical and electronic devices to work and the Car system is no exception. Understanding the chemistry of how a car battery works is another different thing altogether.
Almost everybody knows something about a car battery like the way it’s removed, charged, or stored. But how many people know how car battery works? Very few, I guess. Well, you’re about to get a great insight into How does a car battery work?
How a Car Battery Works
When car ignition is switched ON, a sequence of reactions starts inside the battery, which results in electricity. To maintain this sequence, a device called the alternator keeps generating the electrons as well as storing the ones it can.
It does the generating part with the help of a belt that transmits energy to the battery. Without this sequence of reactions, I’m afraid your car cannot start.
Let’s Show You How It Works Internally
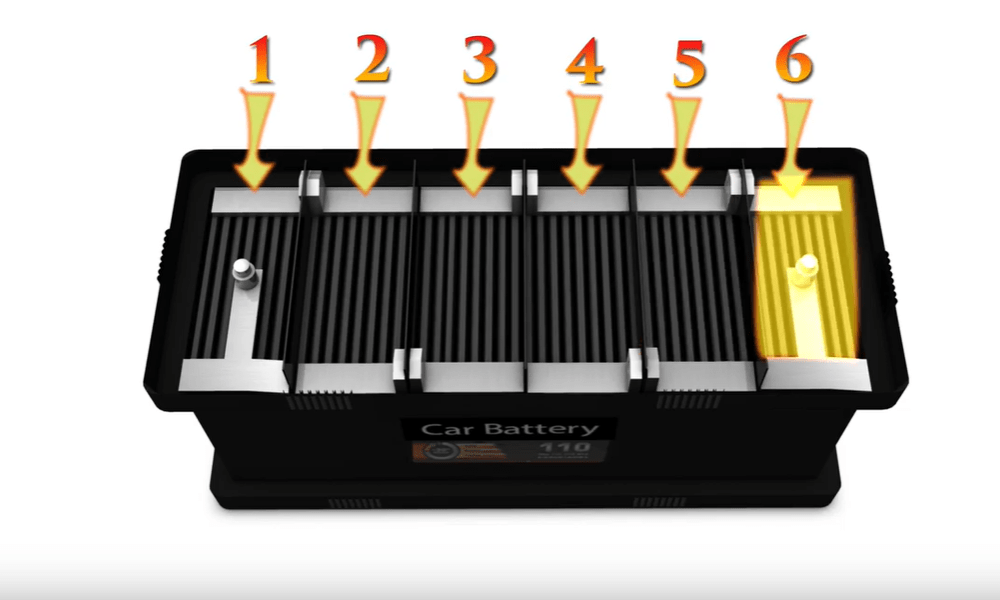
A standard battery contains 12 grids on six SLI battery cells, which means two grids per cell. One of the grids is made up of lead as a single element, and the second grid an oxide of lead. In total, a battery emits 12 volts of power, with each cell emitting two volts.
Both battery grids go into a sulphuric acid solution, which activates a reaction between them. But how the battery work is that the acid solution catalyzes the emission reaction, which produces the ions and lead sulfate.
The resulting ions from the first reaction react with the second grid to give off hydrogen and lead sulfate.
The electrons that come from these series of reactions are what produce the needed electricity that powers the car. This flow of electrons around the cells activates the battery terminals, which transmits it to the whole vehicle through the cables. You can now switch your car on and turn on the stereo.
There is a possibility of a reversal taking place if the alternator is not functioning to charge the battery. To avoid the incidence of a flat battery, ensure that it is charging when the car is working.
Your car battery not only just emits electrons that produce energy, but also uniformizes the supply of electricity to maintain the vehicle’s functioning. It also can store charges for future use.
Structure of a Car Battery
A car battery is not like the cells used in smaller electronic gadgets like the hairdryer. It has six other minor cells that are connected in series. This connection makes the energy from each cell to add up, creating the 12 volts.
The 12 volts comes from each cell (two volts each), although in the correct calculation is 12.6 volts. The principle of emission of energy remains the same. However, some battery models may vary in the volts emitted.
How Does a Car Battery Operate Inside?
The usual method for batteries to function when it’s in connection with an electrical circuit is to emit electrons. Simply put, an electron has a negative charge (the only negative part of an atom), and it plays the most vital role to provide power.
There are crucial things to note in the functioning of a battery. First, the cell contains two terminals, namely the cathode (positive) and the anode (negative). And these terminals go deep into a sulphuric acid solution, reacting with the anode to give off electrons.
Afterward, the cathode sends back these electrons into the solution to maintain a chemical balance. This electron transfer is a whole new reaction between the cathode and the acid, which is different from the first reaction. If there is a flat battery, it means that one of these reactions was incomplete.
The Chemical Reactions in a Battery
In a typical lead-acid cell, there are positive and negative terminals. The positive terminal is the oxide of lead (cathode) and the lead element (anode) the negative terminal. The catalyst known as the acid solution is the sulphuric acid (H2SO4), which forms lead sulfate with the terminals when the battery is in use.
Chemically stating the formula for the reaction
- PbO2 + 4H+ + SO2- + 2e- -> PbSO2 + 2H2O
- Pb + SO2- -> PbSO4 + 2e-
In the set of reactions above, reaction one absorbs electrons while reaction two gives off electrons. And the electrons can only be useful through the terminals that connect to the battery wires.
How Does A Car Battery Charge?
Users will need to charge car battery promptly to prevent it from going flat, that’s why a reliable charging method is necessary. Without this, when the battery supplies the energy required to run a car, it will certainly die.
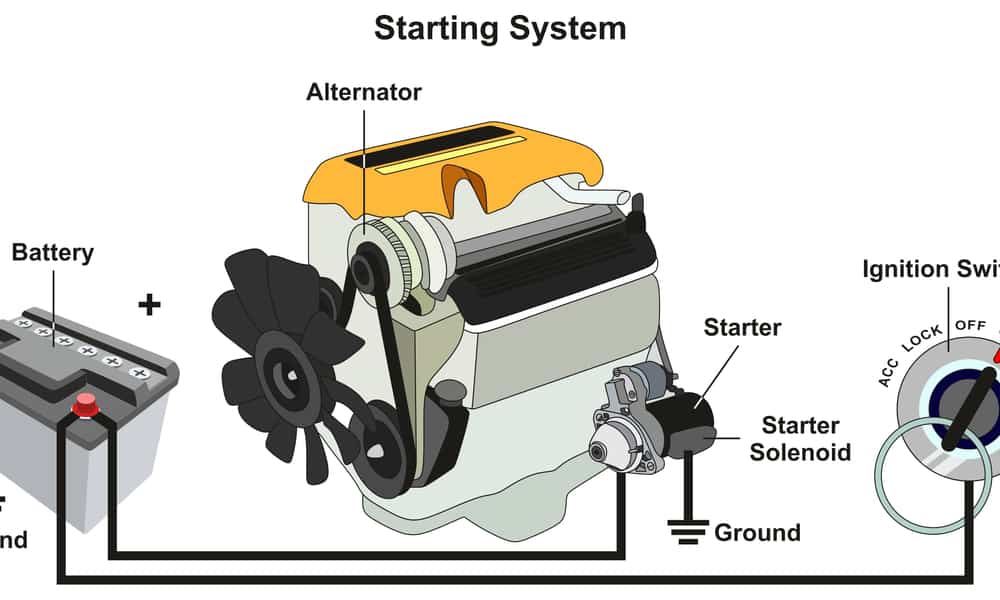
In a typical modern car, the alternator charges the battery while it’s in use. But in older car models, it’s the dynamo carries out the charging duties. Both are dependent on a belt-driven system from the engine that turns the rotor in the alternator cables.
The rotor gains electrons by magnetization of little particles when a copper carbon scratches an iron clip ring on the beam. The turning of the electromagnet inside the stator coil is what produces the electricity inside them.
The flow of electrons that produces electricity is alternating. That means it flows forward and backward, depending on the direction of the rotor. But for better efficiency, it needs to be rectified to make a direct current.
The dynamo works with direct current but not as efficient as the engine speed. But one thing for sure is that it is heavier than an alternator.
When it doesn’t charge properly, the dashboard turns bright indicating a warning sign. This happens most time when the engine shuts down.
How a Car Battery Stores Energy
A quick flow of electrons from the terminals hit the car engine, making the alternator begins to supply electrons. The Volta’s zinc-copper-saline battery does not reverse the electron reaction quickly like the Plante’s lead-lead oxide-H2SO4 battery.
Excessive electrons generated goes into the solution, which gives it off to the terminals to produce electricity. These series of back and forth reaction has been used over time and can be said to be a dependable source of power for cars. It’s so efficient that there hasn’t been a need for a better method.
However, try to keep the environment harm-free by always recycling your old batteries.
How Does A Car Battery Regulates Current?
The alternator produces alternating current, which is turned to direct (rectified) by diodes that permits the flow of electrons in a single direction. The regulator inside the alternator ensures that the supply of voltage is a stable one. Both devices are contained inside or outside the alternator.
Wrap Up
If you have been with us carefully, you must have finally understood how does a car battery work? The battery is an entity of chemical reactions which helps to generate the electricity that is used by the car. Not only does it activate and recycle electrons, but the cell also has a mechanism that ensures it recharges.