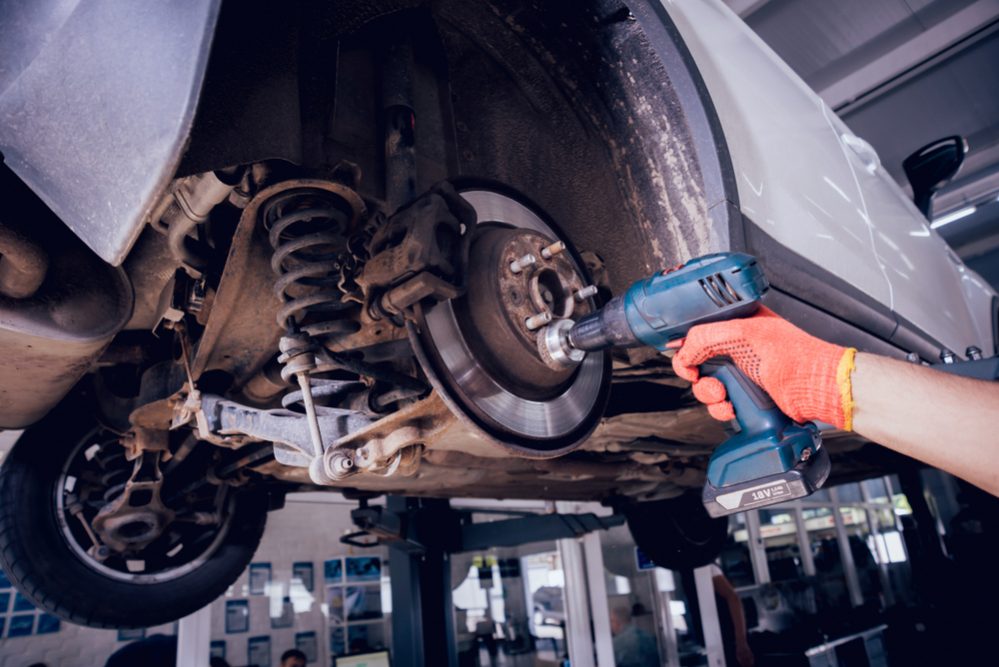
The brakes are the most important active safety of a car and one of its key pieces. However, many drivers do not seem to understand it well.
According to statistics, about 40% of the defects detected by the ITV correspond to the brakes. It is not enough to bring the car to the shop when something goes wrong.
Care should be taken earlier for your car security feature before facing an accident. Have the brakes checked? The braking system is the vehicle’s most important safety item.
External elements that influence the braking
Keep your car in perfect condition during springs. A damping brake System responsible for an increase of 10% in the distance necessary to restrain. Keep an eye on the state and the pressure of your tires because they determine the effectiveness of the braking since one of its missions is to convey the power and braking.
Take into account the state of the road, there are asphalt, which grips better than others, and the weather also affect the efficiency and capacity of the braking. Exercise caution when snow and ice (the adhesion is practically zero) and the first drops of rain, mixed with dust and dirt of the driveway, turned in a strong slider.
In the long journeys should stop and rest every two hours.
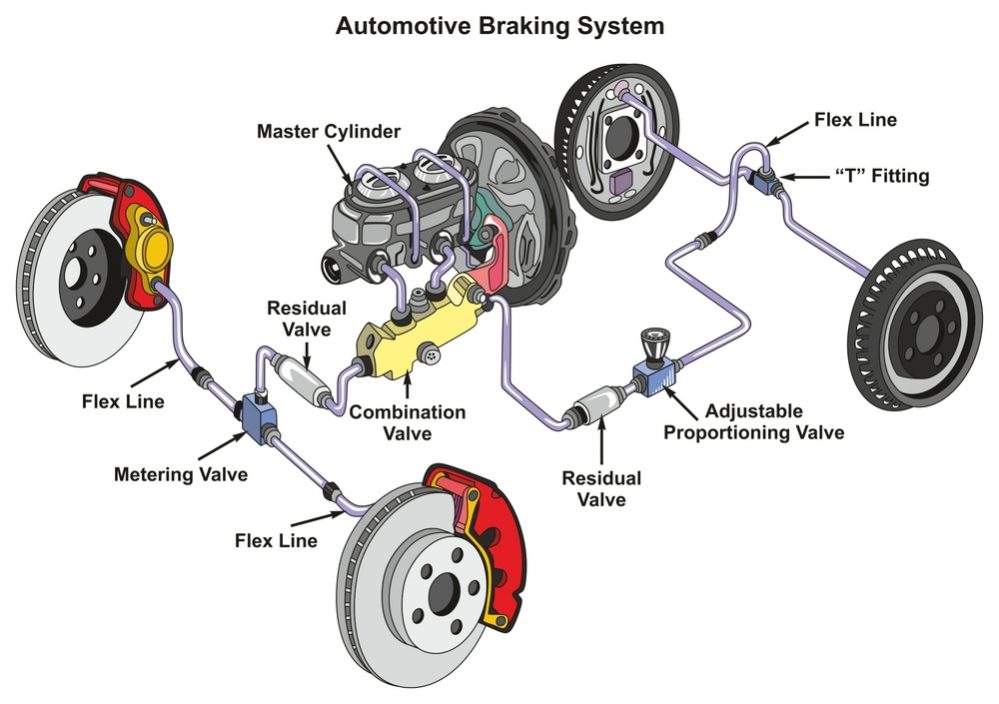
How does the brake system work?
Blaise Pascal was a seventeenth-century French mathematician and philosopher who formulated the principle that a change of pressure at one point of a confined fluid is communicated undiminished to all parts of the fluid. In an automobile braking system, the brake lines are filled with just such a ‘confined fluid’. When pressure is applied via the brake pedal from a piston in the master cylinder, the pressure is transmitted equally to all four brakes.
“Pressure on the brake pedal forces the brake fluid in the master cylinder (the container for brake fluid) through the brake lines to the wheel cylinders to stop the car,” explained Andrew Brown, an auto mechanic with over 25 years’ experience in the motoring world. “One part of the dual master cylinder connects with the front wheels, the other with the rear wheels,” he adds.
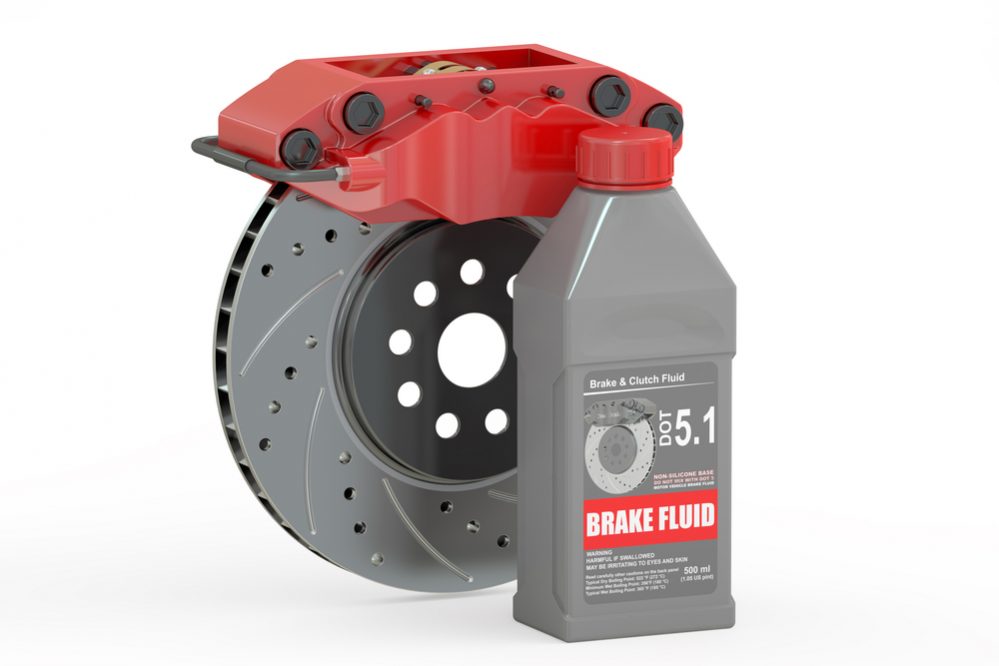
Brake fluid
Brake fluid is hygroscopic which means not only does it absorb water, but it attracts water. Flushing the brake system at a maximum of every 2 years (You’re way off schedule) can save many hundreds or in some cases thousands in brake system repairs over the life of the vehicle. Transmission fluid flushing every 2 years or 24,000 miles can double or triple the life expectancy of modern high-dollar automatic transmissions.
Tips for braking system Maintenance
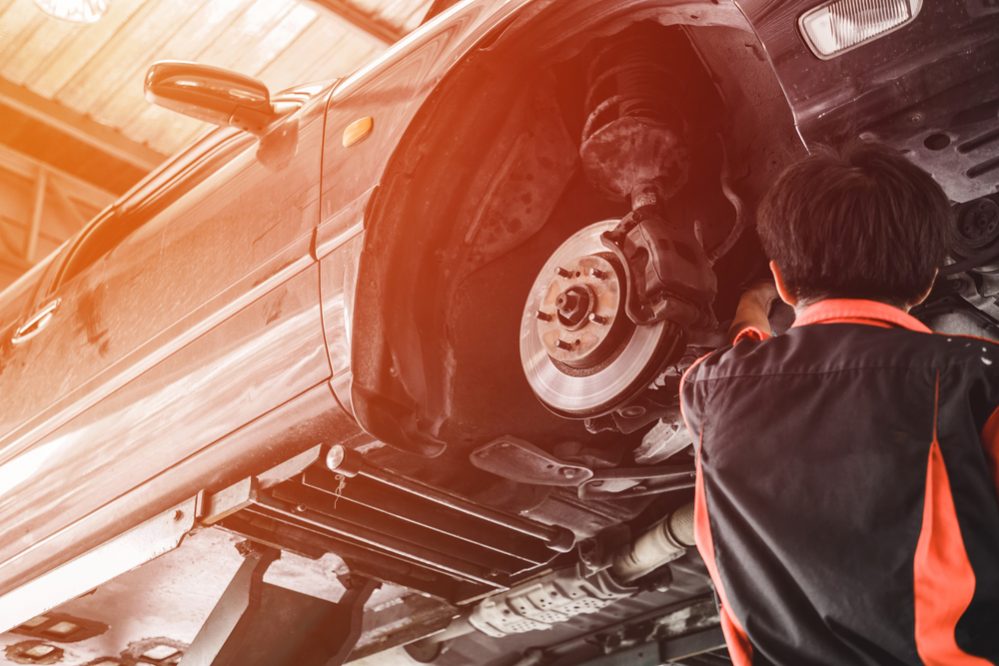
- Verify whenever possible the power of braking of each of the four wheels with a brake meter/brake tester. Don’t forget to check the effectiveness of the circuit.
- Keep the indicated level of brake fluid. Check it often, and replace every two years or 50,000 miles.
- Be sure to review each time the status of brake pads. Their average life is 25.000 km but can become blunt before its hardness and lifestyle.
- You must change the brake shoe (or a shoe or a brake block) for every four changes of brake pads or so.
- Check to see their headlights and brake lights are working. Also, he urges people to make sure to aim the headlights properly.
- Do not modify the original brake system. Observe the times given by the manufacturer.
Symptoms that braking system goes wrong
- If your car may be slowing somewhat because it is little brake fluid, because the pads are worn (in which case you hear a chirping) or because the discs are worn.
- If you brake hard you might have a problem with the servo brake.
- If the car slows down and loses liquid badly it is possible that the brake pump is in poor condition.
- If the car tends to stop the “tilted” check the pressure, the wear, and alignment of the tires. If these are kept in proper condition, which can brake discs are badly located or that the brake adjustment is uneven.
- Also, it can happen that one has strained greasy between the brake pads and the disc, or a flight of liquid or excessively soft damping.
- If you notice the brake pedal is soft it is possible that air in the circuit has been introduced or that the brake liquid is little.
How to Prevent
With conventional brakes
Do not make “hard braking.” In order to restrain of suitable form exert the same pressure on the pedal without getting to the bottom to prevent the wheels are blocked. If this happens, lift a little pressure on the brake pedal to feel that the wheels spin, and then gently press.
With ABS
- The ABS (Anti-Lock Braking System) is a braking system that allows that when stops the wheels, not they block, and therefore they continue turning, which allows that they obey to the turn that is marked to him from the steering wheel.
- The right way to stop a car equipped with ABS brakes is to hit the brakes and did not release pressure until the vehicle is stopped. During braking and subject to activate the ABS, will be felt a vibration in the pedal. This effect is normal, Is the way the car to tell us that the ABS is working.
- It only acts when stepping on the brake with force.
- To obtain an effective braking system must step on the brake pedal with the force from the outset while stepping on the clutch. In performing this maneuver will cause the car to responds to its maneuverability and achieved its arrest in a shorter space.
How do I know that the ABS on my car is running?
Just start the car, turn on a light og ABS signal. The light should turn off after a few seconds. If the ABS does not shut down, it means that the ABS does not work. Still, you can stop the car, but do not have the help of ABS. It would be advisable to bring a workshop to review.
With the change:
- Use the gearbox to slow it is a maneuver can be very useful in prolonged reductions, as they can be the mountain ports.
- Never slow down with clutch into neutral to save fuel.
- Before cutting a shorter running the vehicle must have diminished his speed, since otherwise when it loosens the clutch engine can be passed speed.
- The revision of the brakes must be released once a year of the obligatory way like minimum
Systems that help to restrain
-
- In the maneuvers critics, like the braking in curves or with the wet road or frost, electronic systems of traction control have been designed (ASR/TMC) that detect the moment at which a wheel is going to accelerate itself with respect to the others and reduce the transmitted force the slowing it or combines both actions.
- The dynamic control system (ESP / FDR) prevents slippage of the vehicle in the transverse direction, which keeps track on the curve, and avoids avoid drifting.
- Control of braking in curves (CBC), related to the ABS, offsets any destabilizing the normal movement of the axle under braking into a curve, with a sensitive regulation of the braking pressure at each of the wheels.
Other systems
- BAS (Brake Assistance System), DBC (Dynamic Brake Control), NBA (Nissan Brake Assistance). With these acronyms are identified systems to assist braking developed by various automotive companies. In essence, they are based on strengthening the pressure on the pedal brake when it detects a pisotón. Increase the effectiveness of the ABS, shortening the distance braking.
- Electronic distribution of the braking force. It is an active safety system that distributes braking force between each axle depending on the vehicle load or the state of the road.
- EBV (Electronic Brake-force Variable). Sharing system variable braking. Its operation is equivalent to the EBD
- HDL (Hill Descent Control). Interacts with the ABS to avoid loss of traction in steep declines in vehicles.








I didn’t know that brake fluid absorbs and attracts water. This is important because brake fluid needs to be changed regularly since it has the tendency to be heavy with water. To avoid break problems, I would suggest that Dad gets his brakes checked up monthly to prevent water from accumulating in the fluid. This would mean safe and worry-free driving.
Nice lecture we hope for more
Nice but what are the cause of water been absorbed into the brake filuid. from IWETA KESIENA
I think the main effect that the water would cause of being absorbed into the brake fluid is the concentration at which to pressurize the system. The density of the brake fluid molecule is high than the water molecule and when it mixed up, this lessen the brake fluid density, making it more heavy and weak in pressure.
how to drive